The influence of the Western Mediterranean Oscillation upon the spatio-temporal variability of precipitation over Catalonia (northeastern of the Iberian Peninsula)
Resumen
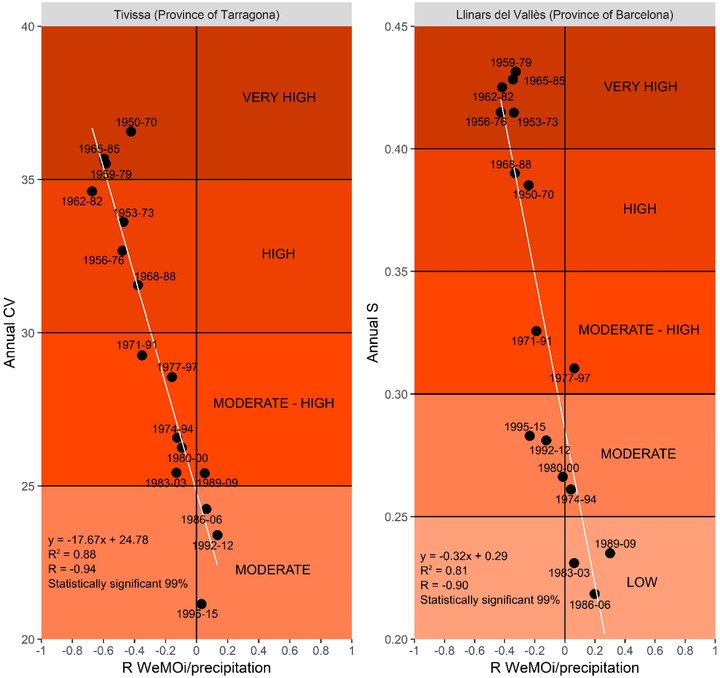
Previous studies have demonstrated the existence of a statistically significant influence of the Western Mediterranean Oscillation index (WeMOi) upon the precipitation of Catalonia (northeast Spain). In the present study, we analyse the statistical relationship between the WeMOi-precipitation correlation coefficients and two statistical indices at the seasonal and annual timescales. The rainfall database used in the analyses comprises 70 pluviometric series covering the 1950–2015 (66 years) study period, and they are spatially distributed throughout Catalonia. The two statistical indices considered are the coefficient of variation (CV) and the disparity consecutive index (S). The results of the spatial variability of precipitation showed the strongest influence of the WeMO over locations in which precipitation irregularity was highest (high CV and S values), and vice versa. The results for temporal rainfall variability showed that in the subperiods in which the correlation coefficients between the WeMOi and precipitation were weak, rainfall variability showed a decrease (low CV and S values), and vice versa. The best results were found to occur in autumn and winter, and in annual rainfall, under the influence of the negative phase of the WeMO. In summer, the positive phase of the pattern shows a predominance due to convective rainfall. The CV and S indices provided high and very high values for rainfall variability on the coast, especially in southernmost Catalonia. The S values are more accurate with regard to identifying the precipitation areas typically influenced by Mediterranean flows. The main conclusion is that the WeMO pattern strongly determines precipitation variability in its areas of influence.